Synthesis of Metal Nano-particle Using SCFs and
Characterization of the Optical Properties of Nano-particles
@Metal particles of nanometer
size are quite interesting objects not only for the application as catalyst but
also for the quantum system composed of small number atoms. The establishment of the synthesis
method of nano-particles with size control is an important topic, and there
have been reported various kinds of methods. Among them, the synthesis of noble metal
nano-particle such as gold, platinum, or silver, by the reduction of ion under
the existence of protective polymer is one of the promising methods. These chemical reductions are ordinary
done with refluxing the solution under the ambient pressure, and the reactions
proceed over several hours. By
utilizing the high-pressure and the high-temperature conditions, we are trying
to regulate the particle size and to improve the productivity.
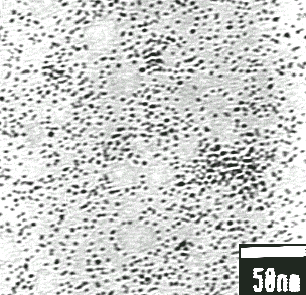 @The figure shows the TEM image of Pt particles
synthesized at 473 K and 5 MPa in solution of water and ethanol mixture with
the protective polymer as PVP. The reaction time was a few minutes, and the
process was quite effective. As is
shown in the figure, the particle size was homogeneous. By changing the solvent, temperature,
and pressure, the particle size and its distribution can be controlled. Besides the platinum particle, it is
possible to make other metal particle such as rhodium and palladium.
@The figure shows the TEM image of Pt particles
synthesized at 473 K and 5 MPa in solution of water and ethanol mixture with
the protective polymer as PVP. The reaction time was a few minutes, and the
process was quite effective. As is
shown in the figure, the particle size was homogeneous. By changing the solvent, temperature,
and pressure, the particle size and its distribution can be controlled. Besides the platinum particle, it is
possible to make other metal particle such as rhodium and palladium.
 @What will happen if we excited this metal
particle by UV light? We are now studying this subject from the view point of
heat detection. The figure shows
the transient grating signal after the photo-excitation (388nm) of this
colloidal solution. After the
photo-excitation, the electron of the metal particle accepts the photon energy,
and then the electron energy is transferred to the matrix vibration of the
particle, and finally transferred to the solvent. The signal can be interpreted by this
two step processes, and the fast process is about 10 ps and the second process
is about 100 ps.
@What will happen if we excited this metal
particle by UV light? We are now studying this subject from the view point of
heat detection. The figure shows
the transient grating signal after the photo-excitation (388nm) of this
colloidal solution. After the
photo-excitation, the electron of the metal particle accepts the photon energy,
and then the electron energy is transferred to the matrix vibration of the
particle, and finally transferred to the solvent. The signal can be interpreted by this
two step processes, and the fast process is about 10 ps and the second process
is about 100 ps.
This is
quite an interesting problem how these time scales are dependent on the
particle size and its environment.
@(This
work is in cooperation with Dr. Harada at